What is a Digital Camera: In today’s fast-moving digital world, capturing moments has become easier and more accessible than ever, and much of that is thanks to the evolution of digital cameras. Whether you’re a professional photographer, a hobbyist, or someone who simply loves documenting life, digital cameras offer powerful tools to create sharp, high-quality images without the limitations of traditional film.
But what exactly is a digital camera, and how does it differ from your smartphone or old film camera? Digital cameras come in various shapes, sizes, and capabilities, each designed to serve different photography needs. From compact point-and-shoot models to advanced DSLRs and mirrorless systems, the options can feel overwhelming for beginners.
In this article, we’ll break down what a digital camera is, how it works, and the different types of digital cameras available today. Whether you’re planning to buy your first camera or upgrade your gear, this guide will help you choose the right one with confidence.
What is a digital camera?
A digital camera is an electronic device that captures photographs and videos using a digital sensor instead of traditional film. Unlike film cameras, which store images chemically, digital cameras convert light into electronic data.
📌Read More👉 What is a Flock Camera?
This data is then processed and saved as digital files, usually JPEG, RAW, or PNG, that you can easily view, edit, print, or share on any device. At the heart of every digital camera is an image sensor, typically a CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) or CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) sensor.
When you press the shutter button, the sensor records the light coming through the lens and transforms it into pixels. The camera’s processor then converts these pixels into a complete image.
Digital cameras are popular because they offer instant results, high-quality images, and flexibility. You can review your shots immediately, delete unwanted images, and capture hundreds or thousands of photos without worrying about running out of film.
Many digital cameras also include advanced features such as autofocus, image stabilization, manual exposure control, burst shooting, and high-resolution video recording.
Today’s digital cameras range from compact, beginner-friendly models to professional-grade systems used in filmmaking and commercial photography. Whether you want to take simple family photos or create stunning artistic images, a digital camera gives you the tools to achieve your creative vision.
Types of Digital Cameras
Digital cameras come in a wide range of styles, each designed to meet different photography needs, skill levels, and budget ranges. Understanding these types will help you choose the right camera for your goals, whether you’re a beginner, hobbyist, or professional photographer. Below are the most common types of digital cameras, explained in detail.

1. Point-and-Shoot Cameras (Compact Cameras)
Point-and-shoot cameras are small, lightweight, and extremely user-friendly. They are designed for everyday photography and casual users who want convenience without worrying about advanced settings.
Key Features:
- Fully automatic shooting modes
- Built-in zoom lenses
- Affordable and portable
- Ideal for travel and family photography
These cameras are less powerful than DSLRs or mirrorless systems, but they offer great portability and ease of use, making them a popular choice for beginners.
2. DSLR Cameras
DSLRs have been the go-to choice for professional and enthusiast photographers for years. They use a mirror and optical viewfinder system that gives a real-time, accurate preview of your shot.
Key Features:
- Interchangeable lenses
- Large sensors for higher image quality
- Superior low-light performance
- Fast autofocus and burst shooting
- Full manual controls
DSLRs are perfect for portraits, sports, wildlife, weddings, and studio photography. They tend to be larger and heavier, but they deliver exceptional performance.
3. Mirrorless Cameras
Mirrorless cameras are modern alternatives to DSLRs, offering similar image quality without the bulky mirror mechanism. They rely on electronic viewfinders or LCD screens for composing shots.
Key Features:
- Lightweight and compact design
- Interchangeable lenses
- Fast autofocus with eye and subject tracking
- Excellent video performance
- Quiet shooting
Mirrorless cameras are popular among travelers, vloggers, videographers, and professional photographers who want power and portability in one device.
4. Bridge Cameras (Super zoom Cameras)
Bridge cameras sit between compact and DSLR cameras. They offer a DSLR-style body with a fixed lens that has a very long zoom range.
Key Features:
- Extreme zoom capabilities (20x, 30x, even 125x)
- Manual shooting options
- Versatile for wildlife and sports
- Fixed lens design
While the image quality may not match DSLRs or mirrorless models, bridge cameras are great for users who want big zoom without changing lenses.
5. Action Cameras
Action cameras are small, rugged devices made for capturing fast-paced activities and adventure sports. Popular brands like GoPro dominate this category.
Key Features:
- Waterproof and shockproof bodies
- Ultra-wide-angle lenses
- Excellent stabilization
- Ideal for biking, surfing, skiing, travel, and vlogging
- These cameras are perfect for on-the-go content creators and thrill-seekers.
6. 360-Degree Cameras
360 cameras capture a full spherical view, allowing viewers to look around in any direction. They’re commonly used for VR content, real estate tours, and immersive videos.
Key Features:
- Dual-lens or multi-lens systems
- Captures everything around the camera
- Great for virtual tours and creative videos
- Perfect for content creators looking to produce innovative, immersive visuals.
7. Instant Cameras
Instant cameras print your photos immediately after capturing them. They combine nostalgia with modern technology, offering both digital previews and physical prints.
Key Features:
- Built-in mini printers
- Fun, stylish designs
- Great for events, parties, and memory books
- Ideal for users who love tangible, old-style photographs.
8. Smartphone Cameras
Though not traditional digital cameras, smartphone cameras have become incredibly powerful, often rivaling point-and-shoot cameras. Modern phones offer multiple lenses, AI enhancements, and excellent video quality.
Key Features:
- Always available in your pocket
- Computational photography for enhanced results
- Great for social media and everyday use
While smartphones cannot replace professional cameras, they are perfect for casual and quick photography.
Each type of digital camera serves a unique purpose, from casual snapshots to professional photo shoots. By understanding these categories, you can choose a device that matches your photography style, skill level, and creative goals.
Key Features of Digital Cameras
Digital cameras have revolutionized photography by offering advanced features that make capturing high-quality images easier and more creative. Understanding the key features of a digital camera is essential for selecting the right device for your needs. Here’s a detailed guide:

1. Resolution: Resolution refers to the number of pixels a camera sensor can capture, usually measured in megapixels (MP). Higher resolution allows for sharper, more detailed images and provides flexibility for cropping or printing large photos without losing quality. While resolution is important, other factors like sensor size and lens quality also impact image clarity.
2. Lens Quality: The lens is the most critical part of a digital camera. High-quality lenses deliver sharpness, accurate colors, and minimal distortion. Digital cameras often offer interchangeable lenses, allowing photographers to choose from wide-angle, telephoto, macro, and portrait lenses for creative flexibility.
3. Sensor Size: The sensor size directly affects image quality. Larger sensors capture more light, richer colors, and better low-light performance, while smaller sensors are less sensitive to light. Sensor size is often more important than megapixels when it comes to image clarity and dynamic range.
4. ISO Range: ISO measures the camera sensor’s sensitivity to light. A wider ISO range allows photographers to shoot in various lighting conditions, from bright sunlight to dimly lit environments. Higher ISO settings enable low-light photography but may introduce noise, while lower ISO settings produce cleaner images in well-lit conditions.
5. Autofocus System: Modern digital cameras use advanced autofocus (AF) systems to quickly and accurately focus on subjects. Features like face detection, eye tracking, and continuous autofocus make capturing moving subjects, wildlife, and sports easier. A reliable autofocus system ensures sharper photos and fewer missed shots.
6. Image Stabilization: Image stabilization helps reduce blurry photos caused by camera shake, especially in low light or when using long lenses. There are two main types:
- Optical Image Stabilization (OIS): Stabilizes the lens or sensor physically
- Digital Stabilization: Uses software to reduce shake
This feature is essential for handheld photography and video recording.
7. Video Capabilities: Many digital cameras offer high-resolution video recording, including 1080p Full HD, 4K, or even 6K/8K. Features like frame rate selection, slow motion, time-lapse, and log profiles provide flexibility for filmmaking, vlogging, or professional video production.
8. Connectivity: Modern digital cameras come with Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and NFC, allowing for instant sharing, remote control, and cloud backup. These features are convenient for photographers and content creators who need to transfer images quickly to smartphones, tablets, or computers.
9. Battery Life: Battery performance is crucial for long shooting sessions. Digital cameras often offer long-lasting batteries capable of capturing hundreds or even thousands of photos on a single charge. Some cameras also support USB charging or battery grips for extended usage.
Understanding these key features helps you choose the right digital camera for your photography style.
From high-resolution sensors and quality lenses to advanced autofocus and video capabilities, each feature contributes to better image quality, creative control, and a more professional shooting experience. Whether you’re a beginner, enthusiast, or professional, knowing these features ensures you maximize your camera’s potential.
What Is a Digital Camera Used For?
The digital camera has evolved far beyond its original purpose of simply replacing film. Today, it is a versatile tool integrated into nearly every aspect of modern life, serving applications ranging from professional artistry to essential scientific documentation. Understanding the diverse uses of this technology highlights its indispensable role in our visually driven world.

📌Read More👉 How Does a PoE Camera Work?
Here is a detailed look at the primary uses and applications of the digital camera.
1. Professional and Commercial Photography
For professionals, the digital camera is the primary tool for earning a living, providing the necessary speed, resolution, and control for demanding commercial work.
- Portrait and Wedding Photography: Capturing life’s significant moments requires high reliability, excellent low-light performance (high ISO), and high-resolution sensors for detailed prints.
- Commercial and Advertising: Cameras are used to create sharp, appealing images of products (product photography), food, and models for advertising campaigns, websites, and print media.
- Photojournalism and Sports: The immediate feedback and high-speed burst shooting capabilities of digital cameras are crucial for capturing fast-moving events and transmitting news photos instantly to media outlets.
- Fashion and Editorial: Capturing high-quality, large-format images for magazines and fashion lookbooks where detail and color accuracy are paramount.
2. Everyday Documentation and Personal Use
The most common use of digital cameras, particularly those integrated into smartphones, is for personal memory keeping and communication.
- Social Sharing: Instantaneously capturing and sharing daily life, travel experiences, and events on social media platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok.
- Memory Preservation: Documenting personal milestones, family gatherings, vacations, and important objects, creating a vast digital archive easily accessible for decades.
- Quick Reference: Taking photos of whiteboards, receipts, documents, or parking locations for quick, non-verbal documentation.
3. Videography and Content Creation
Modern digital cameras are powerful hybrid devices, making them essential tools for content creators and filmmakers.
- Vlogging and YouTube: High-quality 4K and 8K video capabilities, combined with excellent autofocus and portability, make them ideal for creating video content for online platforms.
- Filmmaking: Professional digital cinema cameras and high-end mirrorless cameras are used for shooting short films, documentaries, and even major feature films due to their high dynamic range and customizable formats (like RAW and Log).
- Live Streaming: Using the camera’s high-quality sensor to feed sharp video into a computer for professional-grade live streaming on Twitch, Zoom, or other platforms.
4. Scientific, Industrial, and Specialized Applications
Digital cameras are critical components in fields where visual data capture and analysis are required for research and monitoring.
- Security and Surveillance: Cameras (like CCTV and IP cameras) are used to continuously monitor public spaces, businesses, and homes for safety and security purposes.
- Medical Imaging: Specialized digital cameras are used in dentistry, endoscopy, and ophthalmology to capture internal images for diagnosis and record-keeping.
- Astronomy and Microscopy: Cameras with extremely high sensitivity and long-exposure capabilities are used to capture images of distant galaxies or microscopic details in a laboratory.
- Mapping and Surveying: Digital cameras mounted on drones or aircraft capture high-resolution aerial imagery used for geographical mapping, construction progress monitoring, and agricultural analysis.
5. Education and Training
Digital imaging plays a key role in teaching and demonstrating complex concepts.
- Visual Aids: Creating high-quality images and video clips to illustrate lectures, textbooks, and online courses.
- Virtual Tours: Using 360-degree digital cameras to create immersive virtual tours of real estate, museums, and historical sites.
A digital camera is far more than a device for taking pictures. It’s a powerful tool used for creativity, storytelling, documentation, professional production, and scientific applications. Whether you’re a casual user or a seasoned photographer, digital cameras offer unmatched control, image quality, and versatility.
Advantages of Digital Cameras
Digital cameras have transformed the way we capture moments, offering speed, flexibility, and image quality that smartphones still struggle to match.
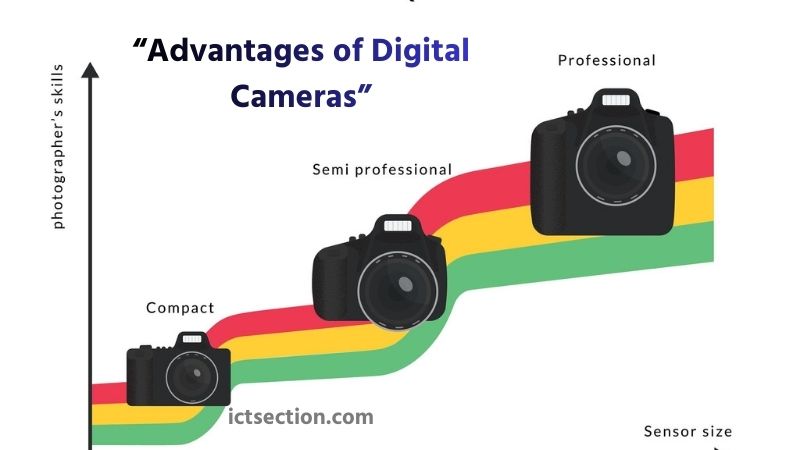
Whether you’re a beginner, hobbyist, or professional photographer, understanding the key advantages of digital cameras can help you choose the right tool for your creative needs. Below are the most important benefits that make digital cameras a powerful choice for modern photography.
- Superior Image Quality: Digital cameras, especially DSLRs and mirrorless models, feature larger sensors compared to smartphones. These larger sensors capture more light, deliver better dynamic range, and produce cleaner images with less noise. This results in sharper details, richer colors, and better low-light performance. Infographic illustration of image quality graph with three types of modern camera such as compact, semi professional and professional.
- Interchangeable Lenses for Creative Freedom: One of the biggest benefits of digital cameras is the ability to swap lenses. From ultra-wide to telephoto and macro to portrait primes, interchangeable lenses allow photographers to control perspective, depth of field, and the overall look of the image.
- Manual Controls for Total Precision: Digital cameras give you full control over shutter speed, aperture, ISO, white balance, and focus modes. This manual control helps photographers experiment, shoot in challenging lighting, and achieve the exact artistic result they want. It’s perfect for learning and mastering photography techniques.
- Better Low-Light Performance: With larger sensors and advanced noise-reduction technology, digital cameras excel in low-light or nighttime situations. You can shoot at higher ISO levels without losing detail or introducing heavy grain. This makes digital cameras ideal for night photography, indoor events, concerts, and astrophotography.
- Faster Autofocus and Shooting Speed: Modern digital cameras offer high-speed autofocus systems with face and eye tracking, making them highly accurate for action photography. Burst shooting modes (like 10–40 FPS) enable photographers to capture fast-moving subjects, perfect for sports, wildlife, or any fast action.
- Greater Dynamic Range: Digital cameras can record more details in both the highlights and shadows. This enhanced dynamic range helps maintain image quality in tricky lighting conditions like bright sunlight, harsh backlight, or strong contrasts.
- RAW Image Capture: RAW files store uncompressed image data, giving photographers more flexibility during post-processing. You can adjust exposure, color, highlights, shadows, and more without losing quality. This is a major advantage over smartphones that mostly shoot compressed JPEG/HEIF images.
- Long Battery Life: Compared to smartphones, digital cameras offer longer battery performance during shooting sessions. This is especially helpful for travel, events, or long outdoor shoots.
- Robust Build and Ergonomics: Digital cameras are designed with comfort, durability, and long shooting sessions in mind. They offer better grips, physical buttons, weather sealing, and stronger construction. These features provide a professional and reliable shooting experience.
- Extensive Storage Options: Instead of relying on limited phone storage, digital cameras use SD, CFexpress, or other memory cards. This allows you to carry multiple cards, shoot in high resolution, and store thousands of photos without worry.
- Versatile Video Capabilities: Most modern digital cameras offer excellent video features, such as 4K/6K recording, high frame rates, external mic support, log profiles, and clean HDMI output. These features make them ideal for YouTubers, filmmakers, and content creators.
- No Distractions While Shooting: Unlike smartphones, digital cameras are dedicated tools. No notifications, calls, or apps interrupt your creative process, helping you stay focused on the shot.
Digital cameras offer a level of image quality, control, and creative flexibility that smartphones still can’t fully match. Whether you’re capturing portraits, landscapes, wildlife, or professional video, a digital camera ensures you get the best results with total creative freedom.
Description of Digital Camera
The digital camera is arguably the most ubiquitous imaging tool of the modern era, fundamentally transforming photography from a chemistry-based process to a data-driven technology. At its core, a digital camera is an electronic device designed to capture still images or video footage by converting light into digital data, rather than using traditional light-sensitive film.
📌Read More👉 How to Clean Camera Sensor: Safely and Effectively
From the compact sensor in your smartphone to sophisticated professional bodies, digital cameras operate on the same fundamental principles, offering unparalleled versatility, instant feedback, and seamless integration with the digital world.
A digital camera functions by combining optical mechanics with advanced electronics. There are three main phases to its operation:
1. The Optical System (The Lens)
The process begins with the lens, which gathers incoming light rays from the scene and focuses them precisely onto the sensor plane.
- Function: Controls three critical elements: Aperture (controlling light intake and depth of field), Focus (ensuring sharpness), and Zoom (changing focal length).
- Significance: The quality of the lens directly impacts the sharpness, clarity, and overall aesthetic of the image.
2. The Imaging Sensor (The Digital Film)
The most crucial component is the image sensor (typically CMOS or CCD).
- Function: The sensor, a grid of millions of light-sensitive pixels, captures the photons passing through the lens. Each pixel converts the light’s intensity and color into a tiny electrical charge.
- Significance: The sensor size and design determine the camera’s ability to handle low light, the range of tones it can capture, and the final image resolution.
3. The Processor and Storage
The final stage involves converting the analog electrical signals into a usable digital file.
- Function: The image processor quickly reads the charges from the sensor, converts them from analog to digital data, processes color, sharpens the image, and compresses the data into a file format (like JPEG or RAW).
- Storage: The finalized digital file is then written to a removable storage medium, such as an SD card, ready for immediate review, sharing, or editing.
The digital camera is a triumph of convergence, blending optics, electronics, and software to provide instantaneous, highly controllable, and cost-effective imaging. It has democratized photography, making high-quality capture accessible to everyone while providing professionals with the precision and speed required by modern media.
FAQs
How does a digital camera work?
A digital camera works by letting light pass through the lens onto an image sensor (CCD or CMOS), which converts the light into digital data. The processor then creates an image file that is stored on a memory card.
What is the difference between a digital camera and a film camera?
Unlike film cameras, digital cameras store images digitally, allowing instant review, editing, and sharing. Film cameras rely on chemical development to produce photographs.
Can digital cameras record videos?
Yes, most digital cameras can record videos in Full HD, 4K, or higher resolutions, with features like slow motion, time-lapse, and professional-grade recording options.
Do digital cameras have manual controls?
Yes, most digital cameras allow you to adjust shutter speed, aperture, ISO, white balance, and focus modes, giving photographers full creative control.
How are digital cameras different from smartphone cameras?
Digital cameras generally offer larger sensors, better optics, faster autofocus, more manual control, and interchangeable lenses, which result in superior image quality compared to smartphones.
Why should I use a digital camera instead of a smartphone?
A digital camera provides professional image quality, creative control, better low-light performance, faster shooting, and advanced video capabilities, making it ideal for photography enthusiasts and professionals.
Conclusion: what is a digital camera
Digital cameras have revolutionized the way we capture and preserve moments, offering unmatched image quality, creative control, and flexibility compared to traditional film cameras or even smartphones. From high-resolution sensors and superior lenses to advanced autofocus, image stabilization, and video capabilities, digital cameras empower photographers of all levels to bring their vision to life.
Whether you are a beginner exploring photography, an enthusiast looking for more control, or a professional producing high-quality images and videos, a digital camera remains an essential tool for creativity, reliability, and precision.
By understanding the key features, types, and functions of digital cameras, you can make informed choices and fully leverage the technology to capture stunning photos and videos every time. Digital cameras are not just devices; they are gateways to unlimited photographic possibilities.
